Skin disorders, such as acne and eczema, vary greatly in symptoms and severity. They can be temporary or permanent and may be painless or painful. Some can be life threatening.
Some skin disorders have situational causes, while others may be genetic. While most skin disorders are minor, others can indicate a more serious issue.
List of skin conditions
ACNE
On the face, neck, shoulders, chest, and upper back, acne is frequently found.
Redness, blackheads, whiteheads, pimples, or painful, deep cysts and nodules make up skin breakouts.
If left untreated, this illness may discolor the skin or cause scars.
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, often known as PIH, can occur in people of color.
COLD SORE
The lips and area around the mouth develop a red, uncomfortable, fluid-filled blister as a result of this ailment. Redness may be more noticeable for those with lighter complexion than for those with darker skin.
Often, the sore will not be noticeable before the affected area tingles or burns.
Additionally, flu-like symptoms like a low fever, body aches, and enlarged lymph nodes may appear during outbreaks.
Cold sores usually look similar on any skin color but can also cause PIH in people with darker skin.
BLISTERS
Any patch of the skin that is watery, transparent, and filled with fluid is what distinguishes blisters.
They can be found alone or in groups and range in size from vesicles, which are smaller than 1 centimeter (cm), to bullas, which are larger.
Anywhere on the body can get blisters.
HIVES
This results in welts that are itchy and elevated after being exposed to an allergen.
Welts may be warm to the touch and barely uncomfortable.
Hives on darker skin may be significantly lighter or darker than your normal skin tone and may appear elevated or irritated. In general, hives are red on lighter skin.
They may be tiny, round, ring-shaped, or shaped randomly.
MEASLES
They symptoms include fever, runny nose, sore throat, red or watery eyes, appetite loss, cough, and these.
Additionally, it results in a red rash that spreads from the face down the body 3 to 5 days after the initial symptoms show. On darker skin, this rash could be more difficult to spot.
The interior of the mouth may develop little red dots with blue-white centers.
Measles may result in People of Color experiencing more pronounced PIH.
Measles causes a rash that spreads from the face to the rest of the body
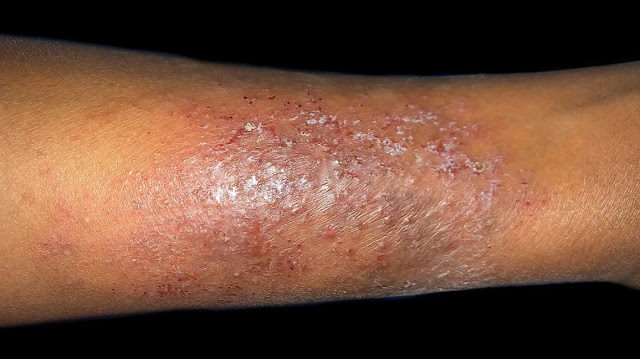
ECZEMA
This is characterized by scaly, peeling yellow or white spots.
Itchy, greasy, or oily patches may be present.
Eczema can result in a red rash on those with light skin. On darker skin, this rash may seem brown, purple, or gray.
The region may also experience hair loss.
PERMANENT SKIN DISORDERS
While some chronic skin disorders develop from birth, others manifest surprisingly later in life.
Sometimes the root cause of certain illnesses is unknown. There are several chronic skin conditions that can be effectively treated, resulting in protracted remission times.
They are incurable, though, and symptoms may recur at any time.
Rosacea, which develops tiny, pus-filled lumps on the face, and psoriasis, which results in scaly, itchy, and dry patches, are two examples of chronic skin disorders.
Vast, erratic patches of paler skin are a symptom of vitiligo.
SKIN DISORDERS IN CHILDREN
Children frequently experience skin conditions. Several of the same skin disorders that affect adults can also affect children. Diaper-related skin issues can also affect babies and toddlers.
Children may also develop skin conditions that rarely affect adults since they are more frequently exposed to other kids and germs.
Typical skin conditions in children include:
- Eczema in babies
- Dermatitis seborrheica
- Shingles,
- Measles
- Warts
- Hives,
- Fifth disease,
- Acne
- Ringworm
- Bacterial or fungal diseases that cause rashes
- allergic reactions' rashes
CAUSES OF SKIN DISORDERS
A few typical known causes of skin conditions aredependable source
- Bacteria in hair follicles and skin pores Fungus
- Parasites, or viruses that live on the skin
- A compromised immune system exposure to irritants, allergens,
- Infected person's skin genetic factors
- Diseases that impact the kidneys,
- Thyroid,
- Immunological system, and other bodily systems
TREATING SKIN DISORDERS
Many skin disorders are treatable. Common treatment methods for skin conditions include:
- Antihistamines
- Medicated creams and ointments
- Antibiotics
- Vitamin or steroid injections
- Laser therapy
- Targeted prescription medications
- Biologics
PREVENTION OF SKIN DISORDERS
Certain skin disorders aren’t preventable, including genetic conditions and some skin problems due to other illnesses. However, it’s possible to prevent some skin disorders.
Follow these tips to prevent infectious skin disorders:
- Wash your hands with soap and warm water frequently.
- Avoid sharing eating utensils and drinking glasses with other people.
- Avoid direct contact with the skin of other people who have an infection.
- Clean things in public spaces, such as gym equipment, before using them.
- Don’t share personal items like blankets, hairbrushes, or swimsuits.
- Sleep for at least 7 hours each night.
- Drink plenty of water.
- Avoid excessive physical or emotional stress.
- Eat a nutritious diet.
- Get vaccinated for infectious skin conditions, such as chickenpox.










Post a Comment